The following is a clinical case of a dermatological disease with systemic repercussions that should be taken into account in the Primary Care consultation.
This is a 55-year-old woman with a medical history of high blood pressure and COPD. She had no allergies, smoked 10 cigarettes a day, and had been on regular treatment with enalapril for the past 6 years and inhaled formoterol for the past 2 years. Due to a worsening of her lung disease, the pulmonologist decided to reinforce her inhalation treatment by discontinuing formoterol and prescribing a combination of indacaterol and glycopyrronium inhaled capsules.
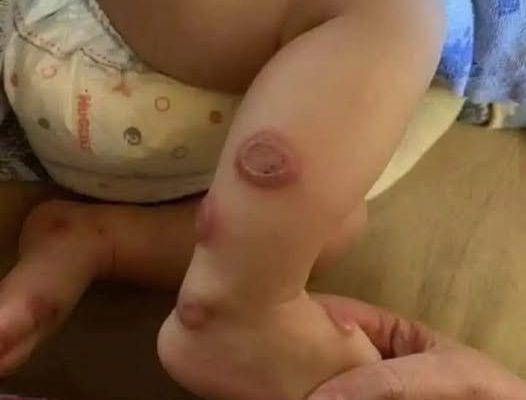
She attended the Primary Care clinic because, on the second day of the new inhaler treatment, she developed painful, erythematous patches on her cheeks and neck, accompanied by a low-grade fever (Fig. 1). The patient denied using any new cosmetics, had not made any changes to her usual diet, and did report sun exposure, albeit with adequate protection. She had not experienced any catarrhal symptoms in the previous days.
An urgent referral to Dermatology was decided for evaluation of the lesions. After being seen by the Dermatology Department, the patient was advised to discontinue the new medication, and a biopsy and blood tests were performed, including a complete blood count, antibodies, lupus anticoagulant, and serology tests. Oral corticosteroids were prescribed.
After 24-48 hours, the lesions diminish in intensity and the pain subsides. Blood tests reveal the presence of leukocytosis with neutrophilia, antibodies, lupus anticoagulant, and negative serology results.
Twenty days later, the results of the skin biopsy arrived and were positive for Sweet syndrome.
Sweet syndrome (also known as acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis) is a dermatological disease classified within neutrophilic dermatoses, since histopathologically it is characterized by the presence of neutrophil infiltrates 1 .
Clinically, it is characterized by the appearance of lesions in the form of erythematous papules or plaques distributed bilaterally, usually asymmetrical, with a sudden onset and pain. The most common locations are the face, neck, upper trunk, and hands. It is also characterized by the presence of systemic symptoms (fever, leukocytosis with neutrophilia, etc.) 2 (Table 1) 1,3 .Table 1.
Diagnostic criteria for Sweet syndrome